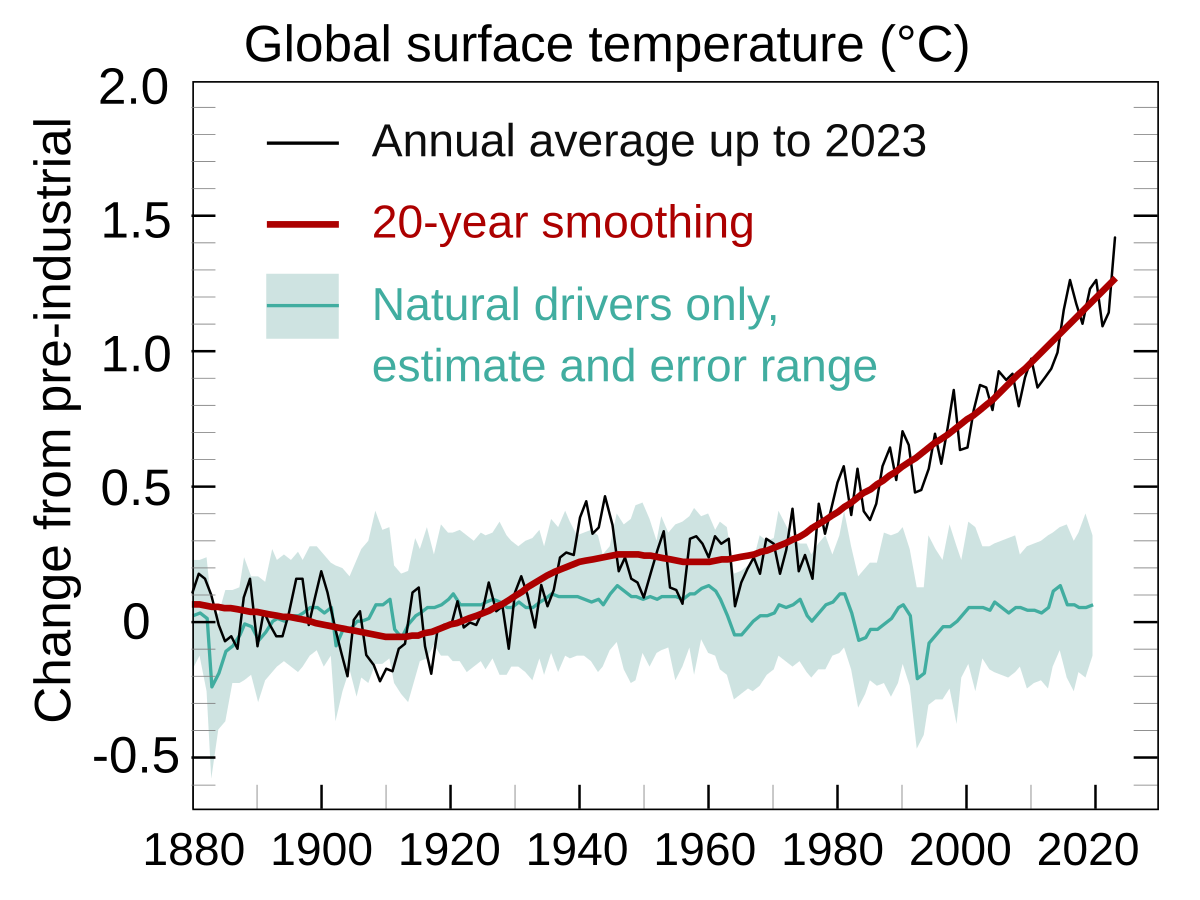
- Attribution of recent climate change is the effort to scientifically ascertain mechanisms responsible for recent global warming and related climate changes on Earth. The effort has focused on changes observed during the period of instrumental temperature record, particularly in the last 50 years. This is the period when human activity has grown fastest and observations of the atmosphere above the surface have become available. According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), it is “extremely likely” that human influence was the dominant cause of global warming between 1951 and 2010. Likely human contribution is 93%–123% of the observed 1951–2010 temperature change. They are like increasing atmoshperic concentrations of green house gasses , for a warming effect, global changes to land surface, such as deforestation, for a warming effect, increasing atmospheric concentrations of aerosols, mainly for a cooling effect.
- Probability density function (PDF) of fraction of surface temperature trends since 1950 attributable to human activity. In addition to human activities, some natural mechanisms can also cause climatic change including for example, climate oscillations, changes in solar activity, and volcanic activity.
- A physical understanding of the climate system: greenhouse gas concentrations have increased and their warming properties are well-established. Historical estimates of past climate changes suggest that the recent changes in global surface temperature are unusual.Computer-based climate models are unable to replicate the observed warming unless human greenhouse gas emissions are included.
- Natural forces alone (such as solar and volcanic activity) cannot explain the observed warming.Factors affecting Earth’s climate can be broken down into feedback and forcings. A forcing is something that is imposed externally on the include natural phenomena such as volcanic eruptions and variations in the sun’s output. Human activities can also impose forcings, for example, through changing the composition of the atmosphere.
- Radiative forece is a measure of how various factors alter the energy balance of the Earth’s atmosphere. A positive radiative forcing will tend to increase the energy of the Earth-atmosphere system, leading to a warming of the system. Between the start of the Industrial Revolution in 1750, and the year 2005, the increase in the atmospheric concentration of Carbon oxide led to a positive radiative forcing, averaged over the Earth’s surface area, of about 1.66 watts per square metre (abbreviated W m−2). An example of internal variability is the El Niño–Southern Oscillation.

(Images/video taken from google/IE)

Recent Comments